|
This article is cited in 8 scientific papers (total in 8 papers)
Proton uptake and proton distribution in perovskite materials for protonic ceramic fuel cell applications
B. Liua, Ch. Liua, X. Zoub, D. Yana, J. Lia, L. Jiaa
a School of Materials Science and Engineering, State Key Lab of Material Processing and Die & Mould Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
b Hubei Institute of Science and Technology Information,
Wuhan, China
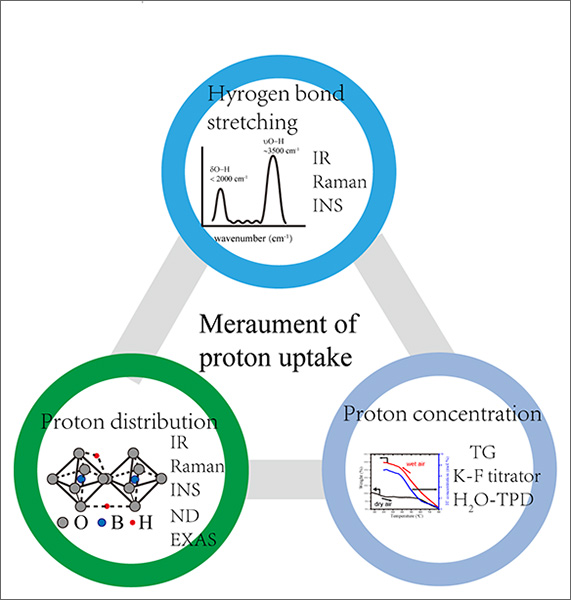
Abstract:
Protonic ceramic fuel cells can generate electric power directly by converting the chemical energy stored in fuels through electrochemical reactions, offering a great potential for practical applications due to their high efficiency, low emissions and fuel flexibility. Lower and intermediate working temperatures (400–700 °C) are prerequisites for the commercialization, but inefficient proton uptake and the conduction ability of electrolyte and cathode materials limits the output performance. In this review, we summarize the common methods used to detect the proton concentration and distribution in some typical proton-conducting perovskites. The infrared absorption and Raman spectra combined with the first-principle calculations could provide the most information about hydrogen bond types with vibrational frequencies at 1000–4500 cm-1, the local proton environment and interactions between proton and crystal defects. The protons in a symmetric environment are easier to transport in the structure compared with that in an asymmetrical and trapped environment. A good understanding of proton uptake and proton distribution features in perovskite materials is necessary to design suitable proton-conducting materials.
The bibliography includes 167 references.
Keywords:
Proton uptake; Wave spectroscopy method; perovskite; cathode and electrolyte material; protonic ceramic solid oxide.
Received: 09.08.2022
Citation:
B. Liu, Ch. Liu, X. Zou, D. Yan, J. Li, L. Jia, “Proton uptake and proton distribution in perovskite materials for protonic ceramic fuel cell applications”, Usp. Khim., 91:11 (2022), RCR5063; Russian Chem. Reviews, 91:11 (2022), RCR5063
Linking options:
https://www.mathnet.ru/eng/rcr4408https://doi.org/10.57634/RCR5063
|


| Statistics & downloads: |
| Abstract page: | 73 |
|






 Contact us:
Contact us: Terms of Use
Terms of Use
 Registration to the website
Registration to the website Logotypes
Logotypes









