|
This article is cited in 9 scientific papers (total in 9 papers)
Fluorine-containing ferroelectric polymers: applications in engineering and biomedicine
V. V. Kochervinskiia, O. V. Gradovb, M. A. Gradovab
a Leading Research Institute of Chemical Technology, Moscow
b N.N. Semenov Federal Research Center for Chemical Physics, Russian Academy of Science (FRCCP RAS), Moscow, Russian Federation
Abstract:
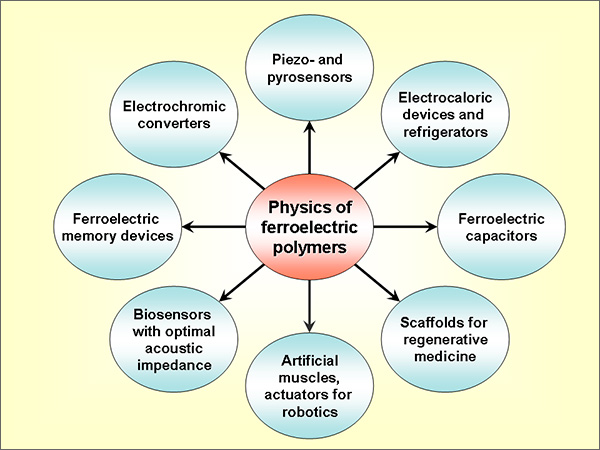
Highly polar fluorine-containing ferroelectric polymers based on vinylidene fluoride refer to the class of electroactive polymers suitable for various engineering applications. Under usual crystallization conditions, polycrystalline texture is formed, while after high-voltage polarization, it is transformed into a non-centrosymmetric structure, which gives rise to high piezoelectric and pyroelectric responses. Such materials can be used for pyroelectric energy conversion. Owing to high impact strength, ferroelectric polymers can serve as materials for alternative energy sources that convert dynamic impact energy into electricity. The non-linearity of electric response (owing to ferroelectricity) and high breakdown fields offer opportunity of using them in capacitive charge storage devices. The intense dynamics of the amorphous phase provides a rapid discharge of the stored energy into an external circuit. In view of the considerable fraction of the amorphous phase (~50%) in fluorine-containing ferroelectric polymers and high dielectric permittivity of the amorphous phase, it is possible to change the system entropy by applying an electric field. In the case of pulsed field, this provides a temperature drop; therefore, these materials (especially as composites) are promising for the design of solid-state refrigerators. The high thermoplasticity of these polymers is useful for the design of sensors \emph{e.g.}, microphones) with a patterned active membrane surface and enhanced characteristics. Biocompatibility and low acoustic impedance (close to the impedance of biological tissues) accounts for the possibility of using these polymers as biosensors. When domains are present in a ferroelectric film, strong local electric fields appear, which can affect the activity of living cells. Using the direct and reverse piezoelectric effect, it is possible to stimulate and control the functions of various tissues, including the nervous tissue.
The bibliography includes 463 references.
Keywords:
ferroelectric polymers, piesoelectric sensors, pyroelectric sensors, ultrasonic generators, alternative energy sources, nanogenerators, capacitive energy storage devices, biological effect of piesoelectric stimulation.
Received: 02.06.2022
Citation:
V. V. Kochervinskii, O. V. Gradov, M. A. Gradova, “Fluorine-containing ferroelectric polymers: applications in engineering and biomedicine”, Usp. Khim., 91:11 (2022), RCR5037; Russian Chem. Reviews, 91:11 (2022), RCR5037
Linking options:
https://www.mathnet.ru/eng/rcr4405https://doi.org/10.57634/RCR5037
|


| Statistics & downloads: |
| Abstract page: | 78 |
|






 Contact us:
Contact us: Terms of Use
Terms of Use
 Registration to the website
Registration to the website Logotypes
Logotypes









